Have you ever considered harnessing the full potential of your laptop by running both Windows and Linux on one machine? In this guide, we dive into the dual-boot setup process, offering clear, step-by-step insights into partitioning your drive, configuring boot options, and establishing a secure system environment. We emphasize the vital preparation steps, such as backing up your data and verifying hardware compatibility, to ensure a smooth and efficient installation. Join us as we explore how this dual-boot configuration can expand your computing flexibility and enhance your productivity.
Prerequisites and Backup Strategies for Setting Up a Dual-Boot System: Windows and Linux on One Laptop
Before beginning the dual-boot setup process, it is critical that we prepare a complete backup and validate hardware compatibility. Dual-booting involves adjusting disk partitions and modifying firmware settings, which can risk data integrity if not preemptively secured. As a precaution, we must run compatibility tests and ensure that both Windows and Linux bootable media are ready for the installation. Taking proactive steps now saves time and safeguards important files from potential loss during partitioning and OS installation.
- Data backup creation
- Downloading the Windows and Ubuntu ISO files
- Creating bootable USB drives using tools such as Rufus or Ventoy
- Verifying system requirements and UEFI/BIOS settings
Following these preparations, we can proceed with confidence. It is essential that we verify UEFI firmware settings to enable the coexistence of both platforms since misconfigurations can result in boot errors. Running hardware compatibility tests by booting the live USB environment for each system is a crucial checkpoint before making any permanent changes. This strategic approach not only minimizes risks but also streamlines the installation process, ensuring that system configurations remain intact and optimal for the dual-boot environment.
By establishing a solid foundation with routine backups and thorough hardware checks, we can tackle the installation steps without unexpected setbacks.
Step‑by‑Step OS Installation Process for Setting Up a Dual-Boot System: Windows and Linux on One Laptop
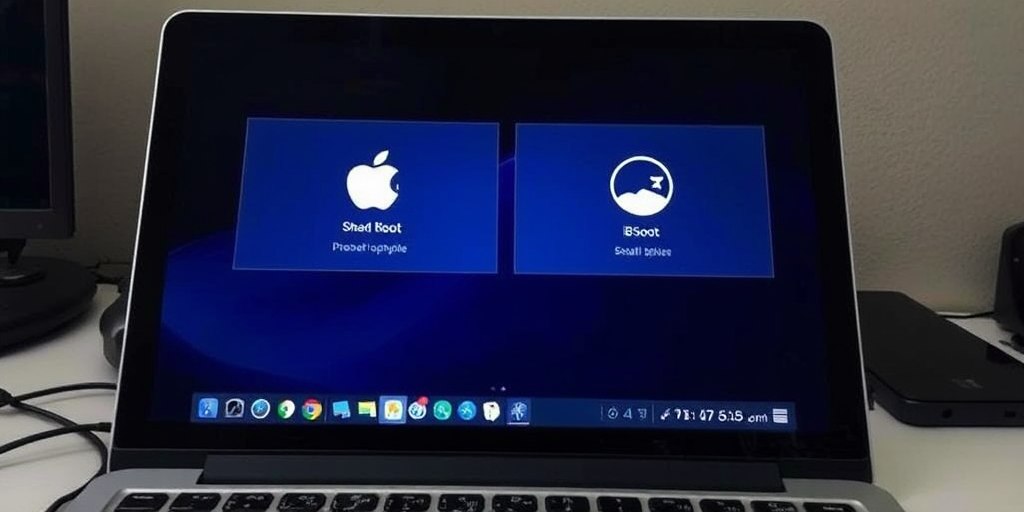
Our installation process begins with a systematic approach to ensure each operating system is installed without conflict. We initiate the process by running the Windows installer, followed by completing its initial setup to stabilize its environment. Once Windows is running smoothly, we prepare the system for Linux by downloading a suitable Ubuntu ISO and creating bootable media. This structured method minimizes errors and ensures that both operating systems are isolated in their dedicated partitions while sharing the same hardware chassis.
- Boot from the Windows installation media and install Windows.
- Boot into Windows and perform initial setup.
- Download the Ubuntu ISO and create bootable media.
- Boot into Ubuntu’s live environment.
- Use the partition slider to allocate space for Ubuntu.
- Install Ubuntu and configure the bootloader.
After completing these steps, we transition to Ubuntu’s live mode where the installation wizard guides us through language selection, keyboard layouts, user credentials, and targeted disk allocation. This step-by-step execution not only prevents overlapping partition issues but also confirms that each phase of the installation adheres to best practices. Clear segmentation between Windows and Ubuntu installation processes is critical to maintaining system integrity and avoiding dual-boot conflicts.
In the final phase, configuring the bootloader becomes essential to ensure seamless access to both operating systems. The GRUB loader, once installed, provides a unified startup screen that allows us to choose between Ubuntu and the Windows Boot Manager reliably. Setting up GRUB correctly is vital, as it manages boot priority, system updates, and recovery settings. Our methodical installation process, coupled with a properly configured boot manager, guarantees that the system remains stable and responsive regardless of the operating system selected at startup.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Setting Up a Dual-Boot System: Windows and Linux on One Laptop
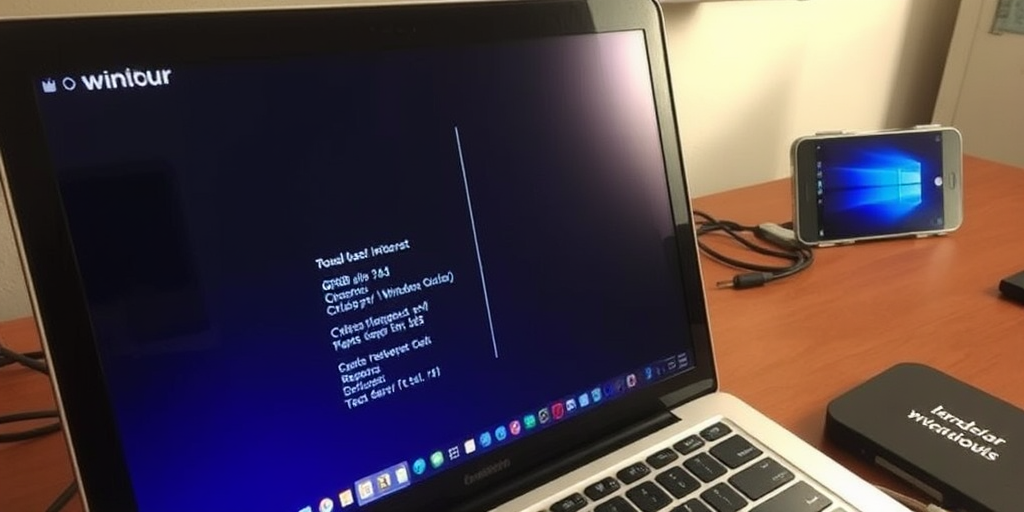
Common error messages during setup may indicate bootloader conflicts, misconfigured partitions, or even underlying hardware compatibility issues. Users might encounter GRUB misconfigurations, partition errors, or timeout failures when the system fails to hand off control from one OS to the other. These early startup failures are typically signaled through cryptic error codes that require careful reading of installation logs to pinpoint the source of conflict. When questions arise like, “What does error code 0x80070005 indicate?” the initial answer should be the exact cause—often permission or compatibility problems. Further explanation reveals that such codes must be cross-referenced with installation documentation to isolate whether the error stems from bootloader misconfigurations or partition mismatches.
- Reviewing installation logs
- Verifying partition allocation
- Updating boot manager configurations
- Checking hardware compatibility
- Using repair utilities
After applying these targeted troubleshooting steps, it is crucial to run complete system updates on both Windows and Ubuntu. Validating backup integrity throughout the process ensures that any critical data remains secure. By systematically reviewing logs, adjusting configurations, and employing repair utilities where necessary, we can address startup sequence errors and secure a stable dual-boot environment.
Final Words
In the action, we explored the essential stages—from prerequisites to troubleshooting—that guide us when setting up a dual-boot system.
We examined how partitioning, OS installation, and boot manager configuration play critical roles throughout the process.
Our discussion on maintenance and performance underscores the importance of ongoing system management.
By following these detailed steps, we reinforce best practices for Setting Up a Dual-Boot System: Windows and Linux on One Laptop, ensuring a reliable and seamless computing experience.
FAQ
Q: What exactly is dual-booting and why should I consider it?
A: Dual-booting allows running two operating systems independently on one laptop. This setup provides access to Windows-specific software while leveraging Linux’s security and development tools.
Q: Should I install Windows or Linux first when setting up dual-boot?
A: Install Windows first, then Linux. Windows creates necessary partitions and boot records, while Linux installations recognize existing Windows setups and configure the boot loader appropriately.
Q: What are the minimum system requirements for dual-booting?
A: For optimal dual-boot performance, you need at least 256GB storage space, 8GB RAM, and a 64-bit processor. Each operating system requires dedicated partition space.
Q: How do I create bootable USB drives for installation?
A: Use tools like Rufus or Ventoy to create bootable USB drives. Download official ISO files for both operating systems and follow the tool’s wizard to format the drives.
Q: What’s the role of GRUB in dual-booting?
A: GRUB (Grand Unified Bootloader) manages the boot process, presenting a menu to select between Windows and Linux at startup. It’s automatically installed with Linux distributions.
Q: How do I partition my drive for dual-boot?
A: Use Windows Disk Management or Linux’s GParted to create separate partitions. Allocate at least 50GB for each operating system, plus additional space for data storage.
Q: What are common dual-boot troubleshooting steps?
A: Key troubleshooting steps include checking boot order in BIOS, verifying partition tables, updating GRUB configuration, and ensuring Secure Boot settings are properly configured.
Q: How do I maintain performance in a dual-boot system?
A: Regularly update both operating systems, manage disk space efficiently, and perform periodic disk cleanup. Monitor system resources and optimize startup programs.



